|
|
|
Facial feminization surgery |
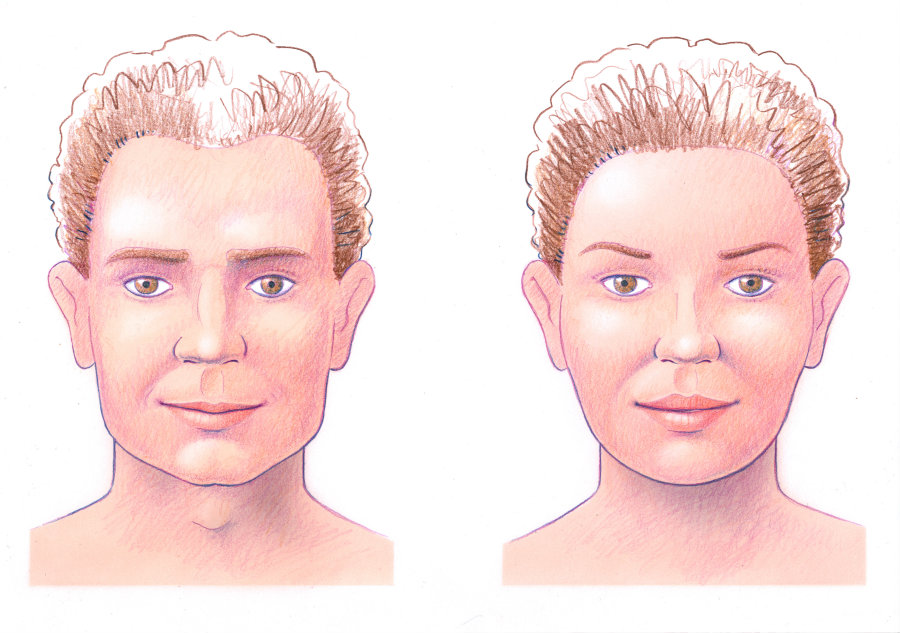
Forehead recontouring
Men tend to have a boney ridge across the forehead just above the eyebrows, which is known as brow (or supraorbital) bossing. This ridge includes the brow ridges (supraorbital rims). Typically, men also have indented temples and a more sloping forehead than women. The female forehead is a nearly vertical line when viewed from the side, and its surface is generally smooth. In contrast, the male forehead is sloped, with prominent supraorbital bossing because of enlarged sinuses. The bossing creates a shallow depression in the glabellar region, which is the area between the eyebrows. When looking at a male face, one's eye is immediately drawn to the hairline, the position and curve of the eyebrows, the frontal bossing and the lateral concavities at the temples.
To tackle all of these features and achieve feminine forehead contours, surgery usually involves a coronal incision (in 7 of 10 cases). This incision follows the hairline. Occasionally, a receding hairline may warrant a pretrichial incision in front of the hairline and scalp advancement. If the hairline continues to recede, hair transplantation will be necessary. Another surgical option is endoscopic shaving of the frontal (forehead) bone and a brow lift. The necessary contouring can be accomplished by either surface planing or osteotomy reconstruction. In addition, calcium phosphate cement (HydroSet) is useful for filling in any concavities.
A smooth frontal bone shape is not the only feature that imparts femininity. The extent to which the forehead as a whole projects over the eyes is important. Overall, eyes are perceived as female or male because of the shape of the surrounding facial bones.
Hairline correction
The hairline is often higher in men than in women, and receding is most pronounced at the corners above the temples. A scalp advancement procedure lifts and repositions the scalp, moving the hairline forward and giving it a more rounded shape. Another option is hair transplantation.
Brow lift
Male eyebrows also differ considerably from female eyebrows. In men, the lateral brow is usually thicker and more horizontal. In females, the lateral brow is thinner and curves upward above the the supraorbital rim, with the highest point at the lateral canthus. It then progressively fades with a gentle downward slope. Raising this lateral brow tail produces a more feminine look.
Orbital recontouring
Eye shape is a key feature differentiating men and women. Female eye sockets tend to be smaller and have a more upward slope laterally. Women's eyes also tend to be closer together at their inner corners and the root of the nose.
Cheekbones
The cheek region is another important area that differs between sexes. Women's cheeks usually have more volume and projection. The female "Pommete" is more of an upside-down pear (hence "poirette"), extending laterally to the corners of the mouth. Augmenting the cheeks with patient-specific implants or fat harvested from other parts of the body is common. Zygomatic valgization osteotomies are another possibility (Mommaerts et al. 1995). Each procedure has potential drawbacks, such as risk of infection with implants, reabsorption of fat over time with fat augmentation, and asymmetric results with osteotomies.
Rhinoplasty
Men tend to have larger, longer and wider noses than women. Producing a more female-appearing nose involves reducing and remodeling the nasal bones and cartilages. Standard rhinoplasty procedures are performed through the nose, using an endoscope. The thick sebaceous nasal skin in men increases the possibility of supratip deformities after surgery, which may need steroid injections or revision surgery.
Lips
Subtle changes to the shape of the lips can make a difference. The distance between the base of the nose and the vermilion border (between the red lip and surrounding skin) tends to be longer in men than in women. When female lips are relaxed, the upper teeth are often exposed by a few millimeters.
Upper lip lifts can address these issues. A curved incision is made just under the alar bases of the nose, a section of skin is removed, and the skin below is undermined up to the vermilion border. Minimal muscle resection and suture suspension prevent the alar bases from stretching downward (Mommaerts & Blythe,2016). Excessive skin can be incorporated into the nose (Mommaerts & Blythe, 2016) or removed.
Chin and jaw contouring
Male chins tend to be higher and broader than female chins. The jawline typically extends outward from the chin at a wider angle in men, and men also have more prominent jaw angles (located below the ears). The chin can be reduced in height, width and projection by a Park & Noah (2008) or Reynecke & Sullivan (2001) osteotomy technique, together with a Reichenbach et al. (1965) osteotomy. Jaw angles can be reduced with botulinus toxin injections, surgical masseter reduction or bony contouring (Mommaerts, 2013). Lateral decortication may reduce the width of the jawline. Another option is mandibular feminization osteotomy (Mommaerts, 2018), which improves all of the aforementioned regions and dimensions in an elegant manner.
All chin and jaw contouring procedures are performed through the mouth, leaving no visible scars. Transition areas are smoothened using a mechanical bone rasp. Chin and jaw contouring procedures may be accompanied by a small risk of damage to tooth roots and temporarily reduced sensation in the chin and lower lip.
Adam's apple reduction
Men tend to have a prominent Adam's apple, which appears during puberty. The Adam's apple can be reduced with a "tracheal shave". The goal of this surgery is to flatten the area without leaving a visible scar. Hence, the procedure is performed using an endoscope and a cartilage shaver. There is a small risk of damage to the vocal cords.
Neck size reduction
When the dimensions of the lower face are reduced, the thick male neck becomes more prominent. A neck narrowing procedure is possible, but few facial feminization surgeons are able to perform this operation, which includes partial resection of the lateral neck muscles.
Associated procedures
Rejuvenation and beautification procedures are often performed at the same time or after the facial feminization surgery. These include neck lifts, filler injections to improve lip volume and definition, upper and lower blepharoplasty, and ZO deep skin peelings. Injectable fillers based on hyaluronic acid have minimal risk (San Miguel Moragas et al., 2016) but tend to be absorbed after about 6 months. Microlipofilling using a person's own fat cells may cause lumpiness and is not long lasting. The longest results occur with temporalis fascia transplantation (Mommaerts, 2013).
|
| |
|
 |
|



